- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Laravel Eloquent ORM for Efficient Database Management
In the world of web development, one of the most powerful features that Laravel offers is its Eloquent ORM (Object Relational Mapping). This feature allows developers to interact with the database in an elegant, expressive, and fluent manner, without needing to write complex SQL queries. Whether you’re building an e-commerce platform, a blog, or an enterprise-grade application, understanding and mastering Laravel’s Eloquent ORM can save you time and effort while improving your application's performance and scalability.
In this blog, we’ll dive into what makes Eloquent ORM so special and how you can leverage it to manage your database efficiently in your next Laravel project.
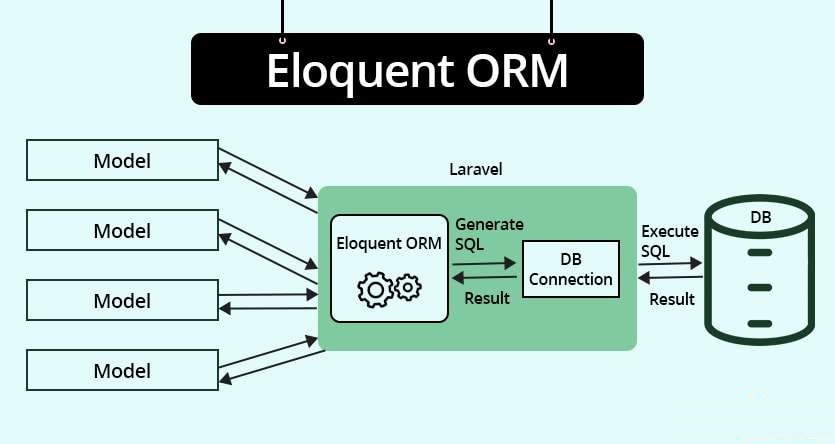 |
What is Eloquent ORM?
Eloquent ORM is Laravel's built-in library that serves as a convenient way of interacting with your database. It provides a straightforward ActiveRecord implementation, which means that each model in your application corresponds to a table in your database, and each instance of the model represents a row in that table. With Eloquent, common database operations—like retrieving, inserting, updating, and deleting records—become easier by using a simple PHP syntax instead of raw SQL queries.
Getting Started with Eloquent ORM
Before diving into the features of Eloquent, let’s take a simple example. Suppose we have a `Post` model that represents a blog post in a `posts` database table.
To define this model, you would run:
bash
php artisan make:model Post
This command creates a `Post.php` file in the `app/Models` directory. By default, Eloquent assumes that the model `Post` corresponds to the `posts` table. It also assumes that each post has a primary key called `id` and timestamps (`created_at` and `updated_at` fields).
Basic Eloquent Queries
Now, let's look at some basic operations.
1. Retrieving Data
Eloquent makes retrieving data simple and intuitive. If you want to get all posts from the `posts` table, you can do so with a single line of code:
php
$posts = Post::all();
You can also apply filters using query methods like `where`:
php
$featuredPosts = Post::where('is_featured', true)->get();
2. Inserting Data
Inserting a new record into the database is also straightforward:
php
$post = new Post;
$post->title = 'My First Post';
$post->body = 'This is the content of my first post.';
$post->save();
The `save()` method saves the new post to the database.
3. Updating Data
To update an existing record, first retrieve it, then modify its attributes and call the `save()` method:
php
$post = Post::find(1); // find post with id 1
$post->title = 'Updated Title';
$post->save();
4. Deleting Data
To delete a record, retrieve the model instance and call the `delete()` method:
php
$post = Post::find(1);
$post->delete();
Relationships in Eloquent
One of the most powerful features of Eloquent is its ability to define relationships between models. Eloquent supports several types of relationships, such as:
- One to One: One blog post has one author.
- One to Many: One blog post can have many comments.
- Many to Many: A post can belong to multiple categories, and a category can have many posts.
For example, if a post has many comments, you can define this relationship in your `Post` model:
php
public function comments()
{
return $this->hasMany(Comment::class);
}
Now, you can retrieve all comments for a post like this:
php
$post = Post::find(1);
$comments = $post->comments;
Eager Loading vs. Lazy Loading
When dealing with relationships, one important concept to understand is the difference between eager loading and lazy loading.
Lazy loading: means that related models are loaded when they are accessed, which can lead to performance issues when dealing with a large dataset.
Eager loading: allows you to load all related models upfront in a single query, improving performance.
For example, eager loading the comments for all posts would look like this:
php
$posts = Post::with('comments')->get();
Eloquent and Pagination
Laravel also makes pagination simple with Eloquent. Instead of manually calculating the offset and limit, you can use the built-in `paginate()` method:
php
$posts = Post::paginate(10);
This will automatically paginate the results and provide links for navigation.
Conclusion
Eloquent ORM is a powerful tool that simplifies database interactions in Laravel. Its expressive syntax and support for relationships make it a go-to feature for efficient database management. By mastering Eloquent, you can focus more on building your application’s features and less on writing complex SQL queries. If you’re working on a Laravel project, such as a blogging platform or an e-learning website, consider leveraging Eloquent ORM to manage your data more effectively. From basic CRUD operations to handling complex relationships, Eloquent has you covered. Happy coding!
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Comments
Post a Comment